-376 ⟶ Division of Jin: End of the Jin State
The states of Han, Wei and Zhao deposed Duke Jing of Jin and...Year
-403
-389
-386
-376
-344
📜 Wu Qi's Reforms in the State of Chu
Wu Qi, the prime minister of the State of Chu, enacts his first series of political, municipal, and martial reforms. Wu Qi gains the ire and distrust of Chu officials and aristocratic elite who are against his crusades to sweep up corruption in the state and limit their power.⟶

Warring States PeriodPolitical ReformMilitary ReformCorruptionAristocracyWu Qi
 China
China🏙️ Handan Founded by the State of Zhao
The Chinese city of Handan is founded by the State of Zhao.⟶
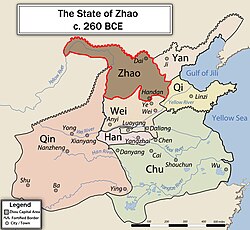
Warring States PeriodCity-StatePolitical DevelopmentUrbanizationEastern Zhou DynastyFoundation
 China
China


